Download the PDF

Following is an article as published in IREI i3 Institutional Investing in Infrastructure, November 2025.
Modernization of energy infrastructure is fast coming into focus as a combination of climate change intensification, inefficiencies related to aging infrastructure, and rising demand may soon prove difficult for existing infrastructure to handle.
While there is global emphasis on the development of new assets to support the energy transition and meet net zero targets, the upgrading of current energy infrastructure is a critical contributor to decarbonization pathways and should not be overlooked or understated.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), energy efficiency is called the “first fuel” in clean energy transitions, as it provides some of the quickest and most cost-effective CO2 mitigation options while lowering energy bills and strengthening energy security.
Moreover, the growing need for resilient infrastructure underscores the importance of energy system modernization as pillars for sustained economic and societal growth. As we continue to see across the world, recent failures in energy systems are rooted in aging and inadequate systems unable to keep up with mounting demand and climatic events.
The modernization opportunity
Investors have the distinct opportunity to capitalize on energy modernization by investing in a range of areas including district energy systems, distributed energy solutions and energy equipment modernization. These technologies can significantly increase energy efficiency and generate financial savings.
In addition, investment along the modernization value chain in opportunities such as heat pumps, thermal energy storage, microgrids and virtual power plants could also provide value as they dovetail with the broader energy transition trend.
At QIC we have been actively contributing to energy modernization and associated efficiency improvements for several years through our portfolio companies.
Creating a low carbon campus at National Western Centre, Denver
A prime example of energy modernization through harnessing efficiency is QIC Infrastructure’s portfolio asset CenTrio’s Energy sewer waste heat recovery system at Denver’s National Western Center (NWC) — one of the first and largest of its kind in the U.S.
Rather than burning fossil fuels, the 250-acre NWC campus system sources up to 90 percent of its district heating and cooling from a recycled source of thermal energy — wastewater — from the city of Denver’s sewer lines. It provides more than 12 megawatts of heating and cooling capacity delivering critical services to municipal buildings as well as Colorado State University Spur facilities.
This innovation in energy infrastructure has transformed the NWC into a modern, sustainable campus environment while advancing the city’s decarbonization goals, reducing carbon footprint by 70 percent, water consumption by 80 percent, and demonstrating innovation, operational excellence and academic collaboration.
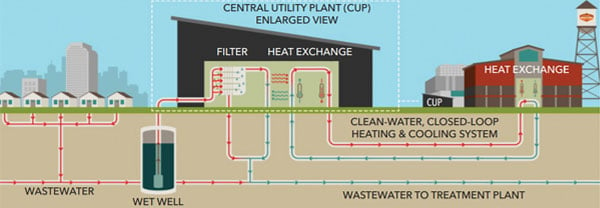 Representative diagram of NWC's district energy system
Representative diagram of NWC's district energy system
Investment outlook
Investing in energy modernization and efficiency improvements continues to gain momentum globally, albeit at different levels regionally. Estimates from the IEA report that investment in energy efficiency has risen by 50 percent compared with 2019 levels — driven in part by policy and regulation, technology deployment, reindustrialization, and international collaboration.
However, the pace of progress requires increased attention and backing via public and private capital. IEA states that investments in energy efficiency would need to triple from $660 billion today to about $1.9 trillion in 2030 to align with the Net Zero Emissions (NZE) scenario.
With the right incentives and support, these efficiency goals are all achievable over time. But by strategically prioritizing scalable and cost-effective modernization solutions, a more secure, affordable and resilient future can be realized sooner.
QIC Infrastructure is a long-term infrastructure investor with an established international platform, an active-management approach and a proven 19-year track record. With an international team of 91 professionals across five offices, QIC Infrastructure manages A$41.4 billion (US$27.1 billion) across 21 international direct investments. QIC is a market leader in the Australian energy transition, managing US$5.2 billion in energy transition assets across Australasia and US$8.5 billion globally (as of June 30, 2025).

